CSS-Position
position 속성
- CSS에서
position속성은 HTML 문서 상에서 요소가 배치되는 방식을 결정한다. position속성은 요소의 정확한 위치 지정을 위해서top,left,bottom,right속성과 함께 사용된다
position: static
-
position 속성을 별도로 지정해주지 않으면 기본값인 static이 적용된다
-
요소들이 HTML에 작성된 순서대로 브라우저 화면에 표시가 된다.
따라서top,left,bottom,right속성값은position속성이 **static**일 때는 무시된다.
<style>
body{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
main {
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
}
div:nth-child(1) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:aqua;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
</style><body>
<main>
<div>1번</div>
<div>2번</div>
<div>3번</div>
</main>
</body>
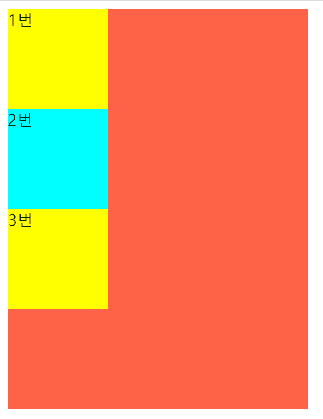
위 결과를 보면 작성된 순서대로 배치 되는걸 볼 수 있다.
position: relative
-
position 속성을 relative로 설정하게 되면, 요소를 원래 위치에서 벗어나게 배치할 수 있게 된다.
-
요소의 위치 지정은
top,bottom,left,right속성을 이용해서
요소가 원래 위치에 있을 때의 상하좌우로 부터 얼마나 떨어지게 할지를 지정할 수 있다.
<style>
body{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
main {
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
}
div:nth-child(1) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:aqua;
opacity: 0.8;
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
</style><body>
<main>
<div>1번</div>
<div>2번</div>
<div>3번</div>
</main>
</body>
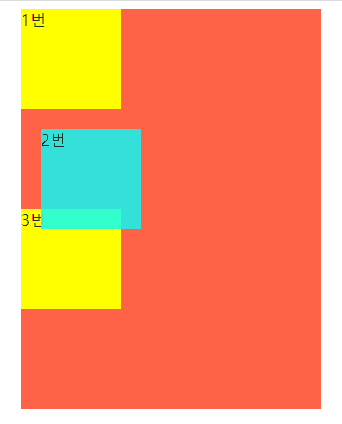
position: absolute
-
position속성이absolute일 때 해당 요소는 배치 기준을 자신이 아닌 상위 요소에서 찾는다. -
부모 요소(가장 가까운 상위 요소)를 기준으로
top,left,bottom,right속성을 적용해야 힌다. -
기준은
position이relative또는fixed또는absolute인 부모가 된다. 보통 부모요소에position:relative를 부여한다.
<style>
body{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
main {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
}
div:nth-child(1) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:aqua;
opacity: 0.8;
position: absolute;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
</style><body>
<main>
<div>1번</div>
<div>2번</div>
<div>3번</div>
</main>
</body>
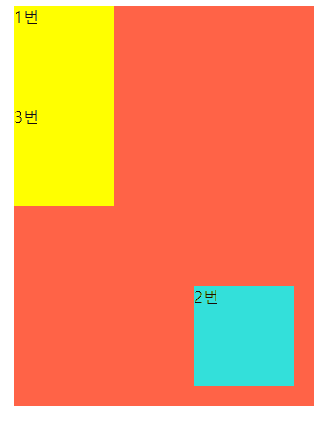
-
위 결과를 보면
div의 부모는main이기 때문에 main 영역 안에서 독립적으로 작용하는걸 볼 수 있다 -
위 코드에서 main에
relative를 적용하지 않는다면 아마 웹 브라우저 우측 하단에 2번재 div가 출력되는걸 볼 수 있을것이다
position:fixed
-
fixed는 요소를 고정하는데 사용된다.** -
fixed의 배치 기준은 자신이나 부모 요소가 아닌 브라우저 전체화면이다. -
웹사이트를 보면 카테고리를 포함한 상단이 스크롤을 내려도 고정되어있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
<style>
main {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
margin: auto;
}
div:nth-child(1) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
}
div:nth-child(2) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:aqua;
opacity: 0.8;
position: fixed;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
}
div:nth-child(3) {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
</style><body>
<main>
<div>1번</div>
<div>2번</div>
<div>3번</div>
</main>
</body>
위 결과를 보면 2번째 div가 독립적으로 작용되어 main이 기준이 아닌 브라우저 전체화면이 기준이기 때문에 우측 하단에 고정되어 있는걸 볼 수 있다.
position: sticky
-
sitcky속성은 필수적으로top,bottom,left,right중에 하나를 필수적으로 설정해야한다.** -
sitcky로 설정된 영역은 설정된 위치(예 top: 0px)에 도달하기 전까지는
static속성처럼 행동하다가 설정된 위치에 다다르면fixed속성처럼 행동하는 속성이다. -
아래의
overflow속성들 중 하나를 필수로 적용해야한다.-
overflow: hidden -
overflow: scroll -
overflow: auto
-
sticky에 대해서 추가 사항은 아래글은 참고하면 좋을거 같습니다!